|
Discovering prehistory (as well as contemporary and avant-garde) is an opportunity for questions about what belongs and what does not belong to art. It seems reasonable to assume that any strictly utilitarian remnants of prehistoric cultures (tools, weapons, habitat) belong to the history of civilization, and to art history include those which have no useful function and are associated either with magic (or religion), or burial dead, which is closely associated with magic, or, finally, the man hardly explainable tendency to ornament decorating.
With these assumptions may be classified as prehistoric art:
PETROGRYPHS, CAVE PAINTINGS, SCULPTURES, CERAMICS, MEGALITHIC STRUCTURES
with the following caveat: the megalithic monuments include Stonehenge, and even some buildings in Malta (although they belong to the culture of the Aegean), but you can not them include either the Mycenaean fortifications, even less of the pyramids of Egypt, in which the machining precision and sophistication of design point to a much later stage of human development. Rather, we include such structures to early antiquity. |
|
Probably all processes in the history of humanity follow the same pattern. At first, taking their time, the features of a new concept are born; then, a sudden acceleration takes place and in no time these features mature and start to dominate. Almost at the same time the first features of a subsequent formation begin to appear.
The Stone Age was a period of about two million years which lasted till the Bronze Age, that is, till the uprising of the first great civilizations. During that time, the humankind came into existence and reached the stage of being able to undertake artistic activities. However, according to the presented outline, 98 per cent of time this process took passed on the forming of species. When it already reached maturity, shortly it also reached the summit of artistic performance in sculpture and painting.
The Stone Age is divided into three periods: the Paleolithic, the Mesolithic and the Neolithic. The Chalcolithic (Copper Age), also called the Eneolithic (Bronze Age) is, depending on the context, either the last phase of the Neolithic or the preliminary phase of the Bronze Age. From a general historical perspective the first three periods are essential, the Paleolithic being the most important of them. It was during the Paleolithic when people created the first works of art.
The Paleolithic, i.e. the Early Stone Age, has lasted for over two million years and it is divided into three periods. Their dating has a very approximate character since the oldest cultures that had emerged at the beginning of the lower Paleolithic were dying out till the half of the middle Paleolithic.
In West-European studies, “Upper Paleolithic” refers to the history of Europe; however, the same period in the history of Africa is called “Late Stone Age”. The division of the Stone Age into the Paleolithic, the Mesolithic and the Neolithic is based on a production technique of the stone tools. It refers to knapped stone tools (Paleolithic), microliths (Mesolithic) and smoothed stone (Neolithic). It is a very general division and reveals little about the development of the humankind, and even less about the art history, which was born in the final phase of the Paleolithic.
Anthropologically speaking, the Lower Paleolithic is the Homo erectus' era, the Middle Paleolithic is the Neanderthal man's era, and the Upper Paleolithic is the epoch of the Cro-Magnon man.
The art history starts in the Upper Paleolithic and is connected with the history of the Cro-Magnon man. It had its center in the so-called Franco-Cantabrian region: southern part of today's France, the Pyrenees and the north coast of today's Spain (Cantabria). A majority of the most important archeological excavation sites is situated there, those in which the traces of main paleolithic cultures were discovered, as well as the examples of fantastic cave paintings of the Magdalenian culture. Among them: Altamira caves, Lascaux, Chauvet, Aurignac (the Aurignacian culture), La Gravette (the Gravettian culture), La Madeleine (the Magdalenian culture) etc.
Why the paleolithic art, wonderfully developing in the area of Western Europe, quite suddenly ended (which means its authors died out), and soon an equally wonderful though completely different art flourished in a distant, mesolithic Göbekli Tepe (borderland of Syria and Anatolia), thousands of kilometers away? It remains one of the greatest riddles of art history. |
PETROGLYPHS
Petroglyphs are images of humans, animals and ornaments engraved (not painted) in the rock material.
(about 10 000 BC)

Nadro, Brescia, Italy

Gilf-Kebir, Egypt

Po-Toi, Hong Kong

Qobustan, Azerbaijan, 8000 BC

Qobustan, Azerbaijan, 8000 BC
/w tym przypadku archeolog mógł sobie darować walkę z czasem.../

Twyfelfontein, Namibia /there probably also.../
SCULPTURE

|

|
Wenus of Tan-Tan
Marocco,
400 000 BC |
Wenus of Berekhat Ram
Golan Heights, 230 000 BC |
/the oldest objects made by human hands - so far as.../
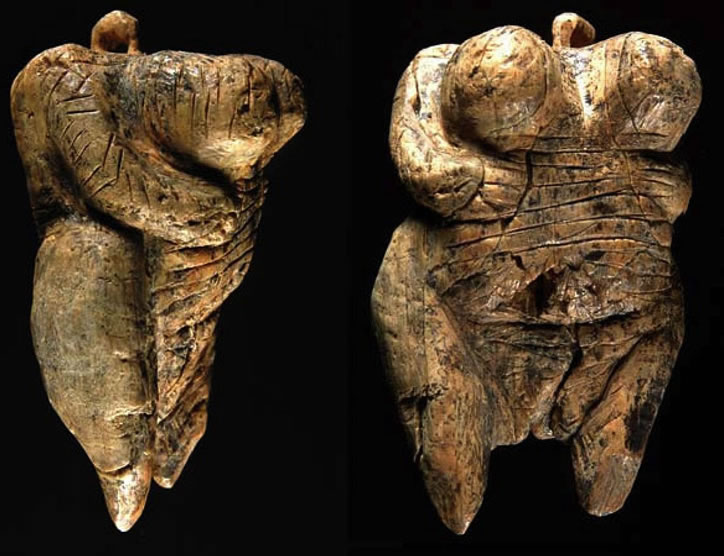
Venus of Hohle Fels, Schelklingen, Germany, 40 000 BC
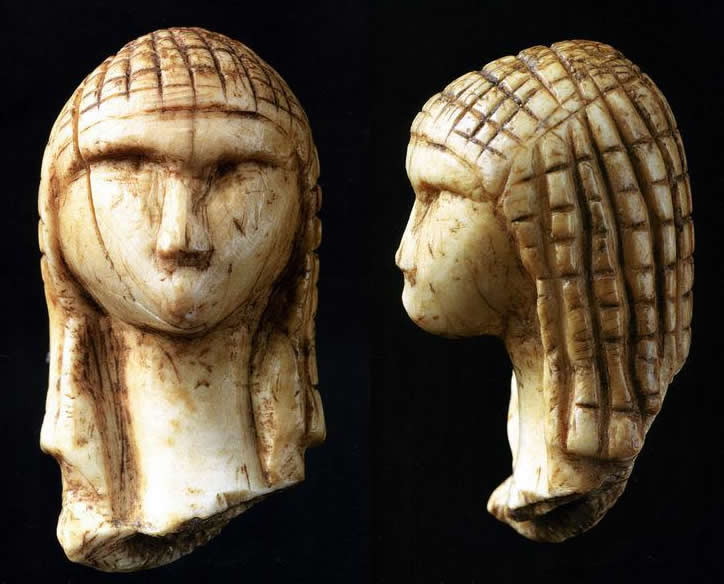

Venus of Brassempouy, Francja, 30 000 BC
/I think - by the detail design and hairdo - especially compared with her neighbours - a very dubious dating/

|

|
|
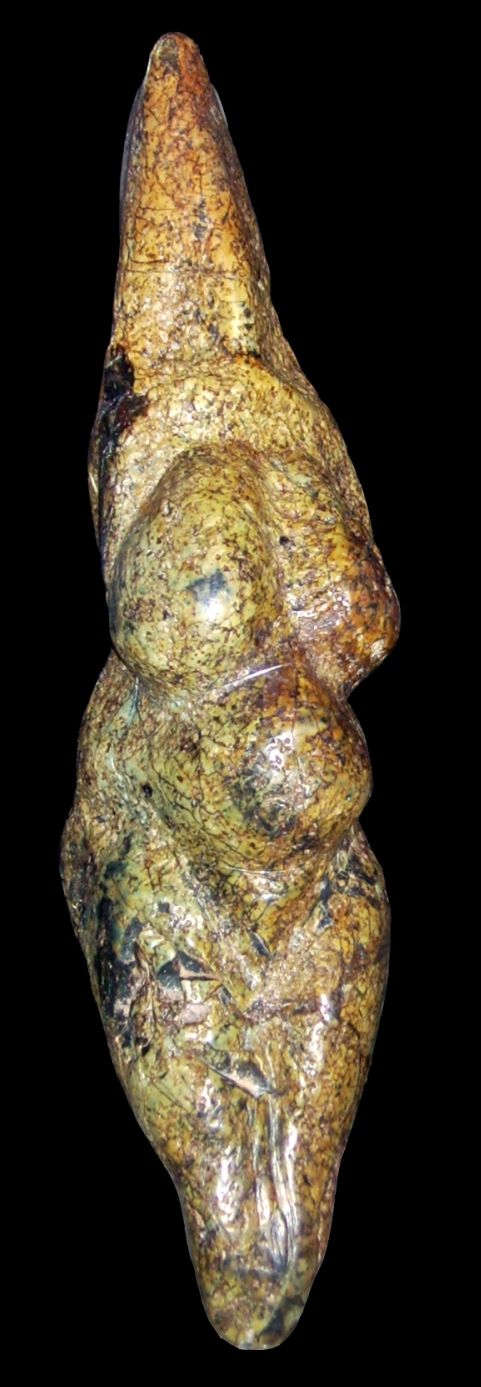
Wenus of Dolni Vestonice,
Morawa
29 000 BC |
Venus of Laugerie Basse
Francja |
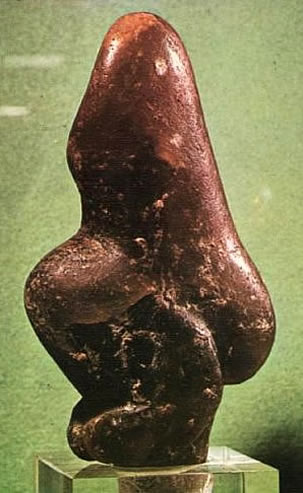
Venus of Savignano
25 000 BC |
|

|
Venus of Tursac,
22 000 BC |
Venus of Willendorf,
22 000 BC |

Venus of Lespugue, 20 000 BC

|

|
Venus of Laussel,
19 000 BC |
Venus of Gagarino,
Ukraine |

Mother Goddess of Çatalhöyük, 7400-7300 BC
CAVE PAINTINGS
Altamira, Spain, 15 000 BC


Lascaux, France 15 000 BC












Niaux, France

Chauvet, France, 30 000 BC




/frankly, it's hard to believe that the chiaroscuro paintings created over 30 000 years ago .../
MEGALITHIC STRUCTURES
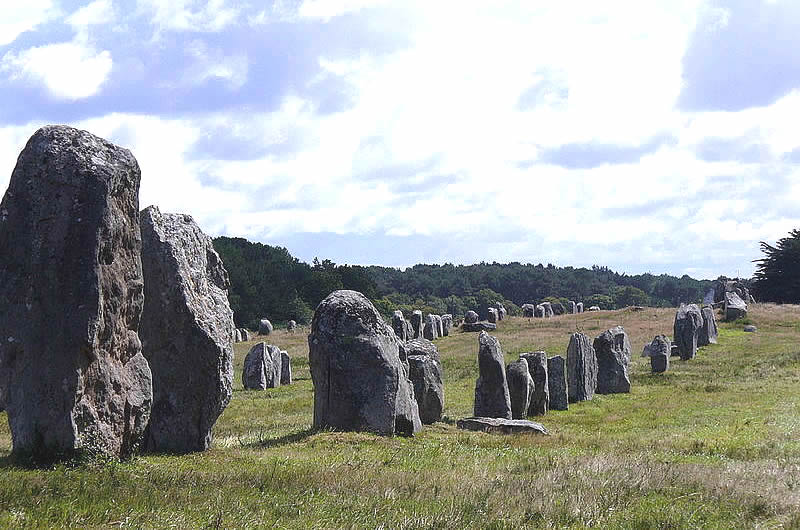

Carnac, France, 4000 BC
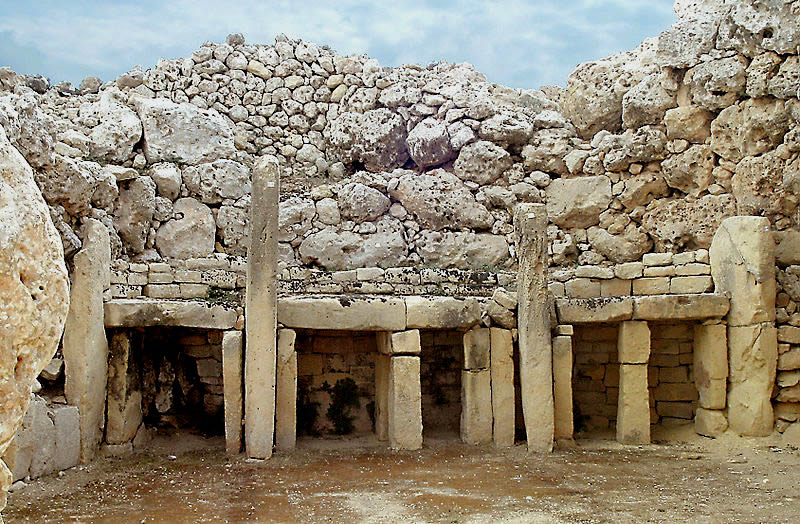

Ggantija, Malta, 3600 BC

Tarxien, Malta, 3500 BC

Hagar Qim, Malta, 3000 BC

New Grange, Irland, 3200 BC

Ta Hagrat, Malta, 3000 BC
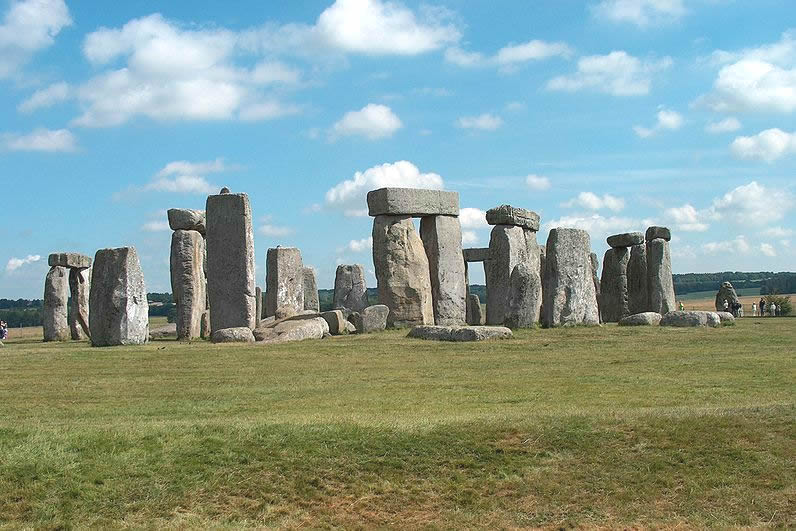

Stonehenge, England, 2900 BC

Pyramid of Khufu, Gizeh, 2950 BC

Lion's Gate, Mycenae, 1250 BC
CERAMICS

Linear Pottery culture, 5500 BC

Comb Ceramic culture, 3000 BC
 
Catacomb Graves culture, 2800 BC
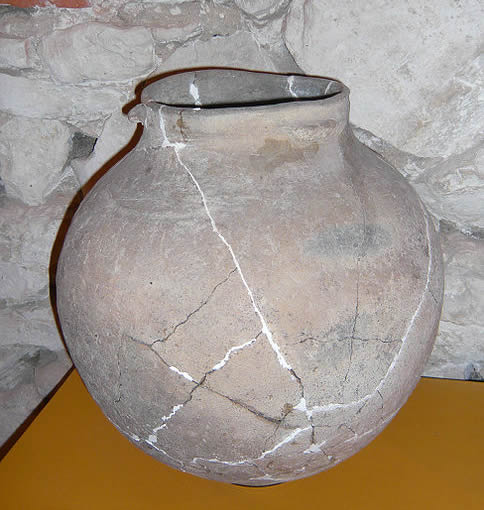

Globular Amphora culture, Krasnystaw, 3000 BC


Stroke-ornamented ware culture, 6000 BC
 
Corded Ware culture, 3000 BC

Funnelbeaker culture, 3700 BC |
|

